Deploy Docker n8n, API backend for WHMCS/WISECP
Setting up n8n workflow
Overview
The Docker n8n WHMCS module uses a specially designed workflow for n8n to automate deployment processes. The workflow provides an API interface for the module, receives specific commands, and connects via SSH to a server with Docker installed to perform predefined actions.
Prerequisites
- You must have your own n8n server.
- Alternatively, you can use the official n8n cloud installations available at: n8n Official Site
Installation Steps
Install the Required Workflow on n8n
You have two options:
Option 1: Use the Latest Version from the n8n Marketplace
- The latest workflow templates for our modules are available on the official n8n marketplace.
- Visit our profile to access all available templates: PUQcloud on n8n
Option 2: Manual Installation
- Each module version comes with a workflow template file.
- You need to manually import this template into your n8n server.
n8n Workflow API Backend Setup for WHMCS/WISECP
Configure API Webhook and SSH Access
-
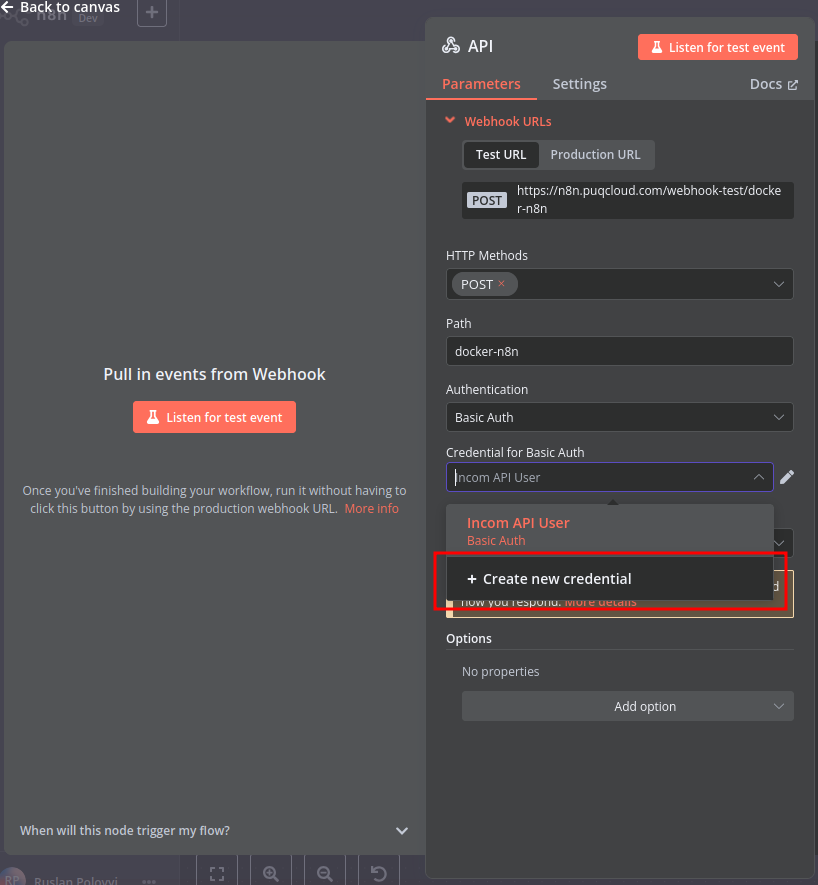
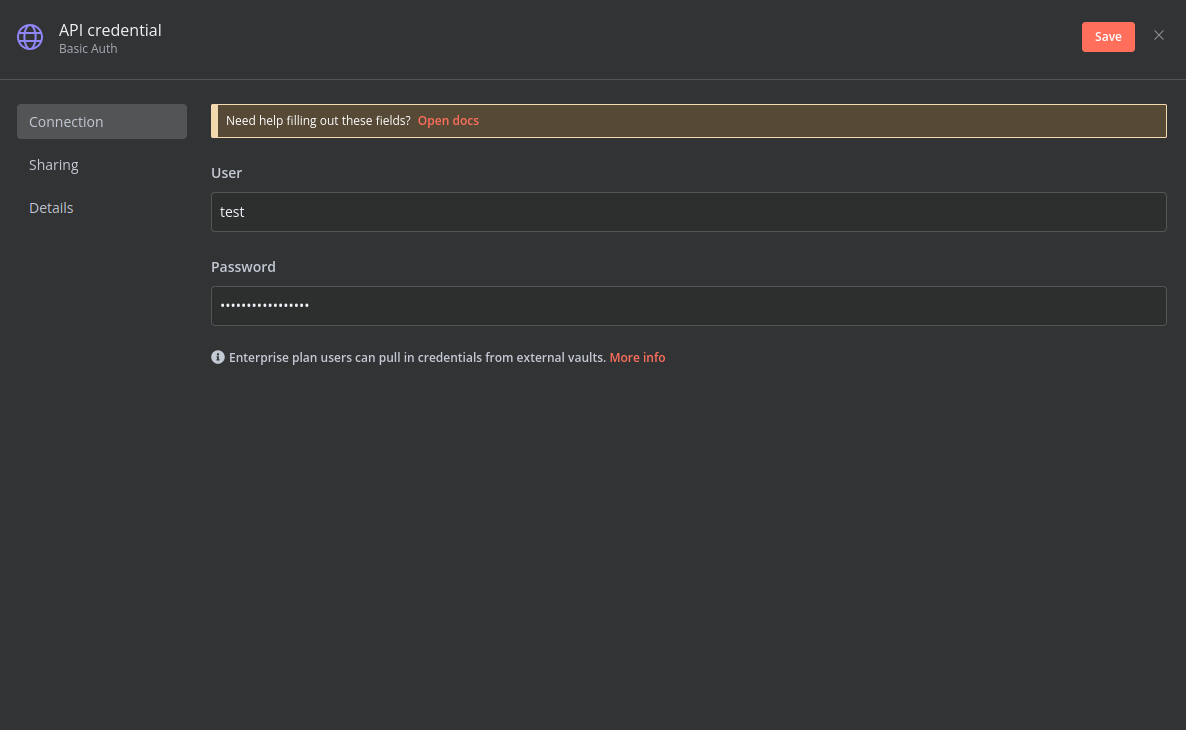
Create a Basic Auth Credential for the Webhook API Block in n8n.
-
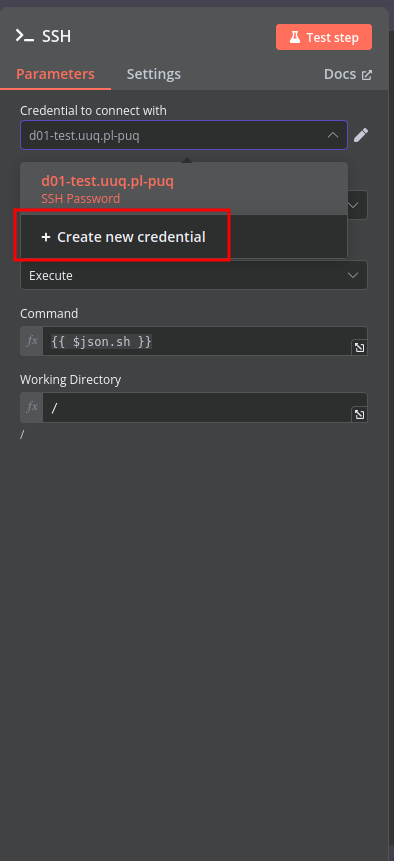
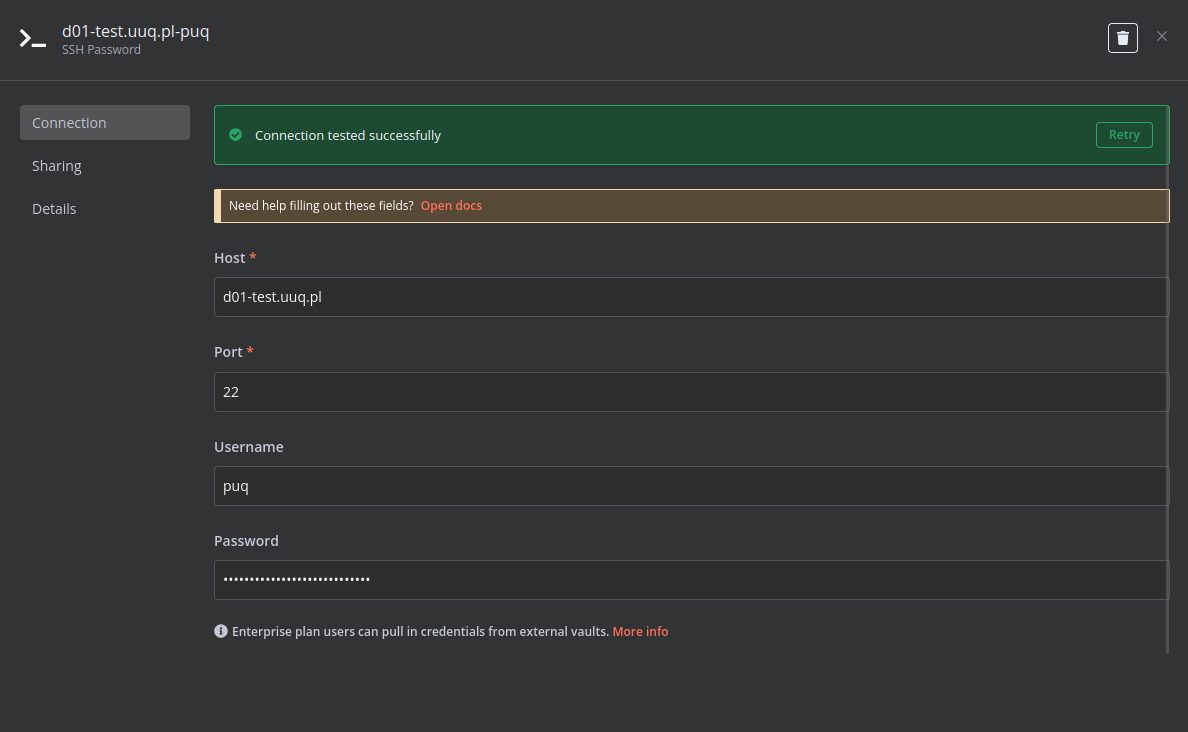
Create an SSH Credential for accessing a server with Docker installed.
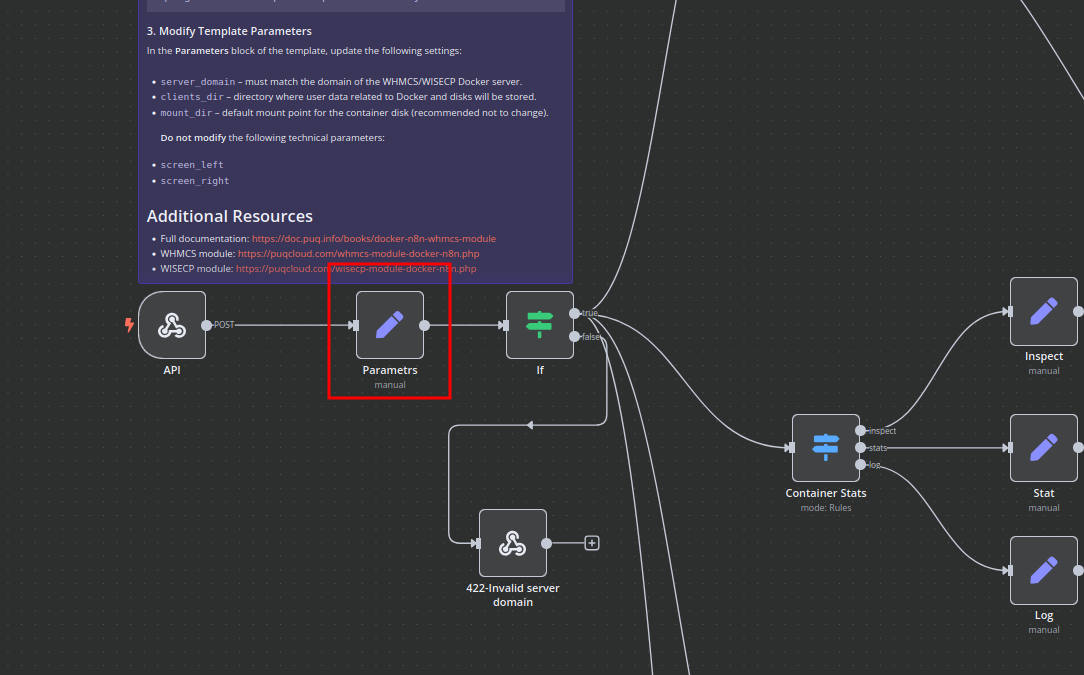
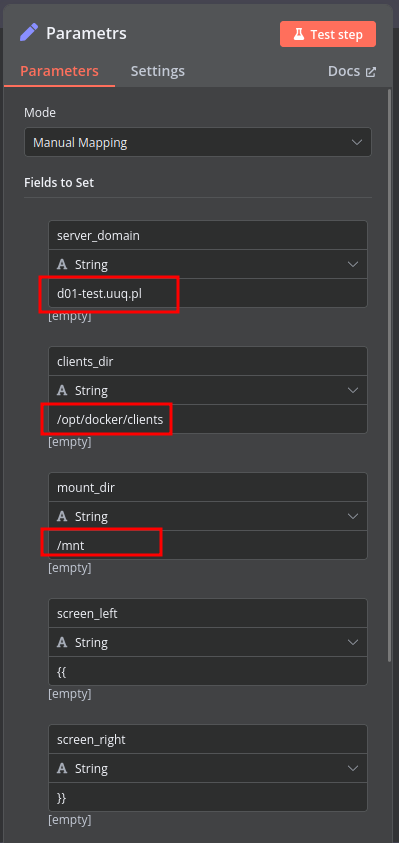
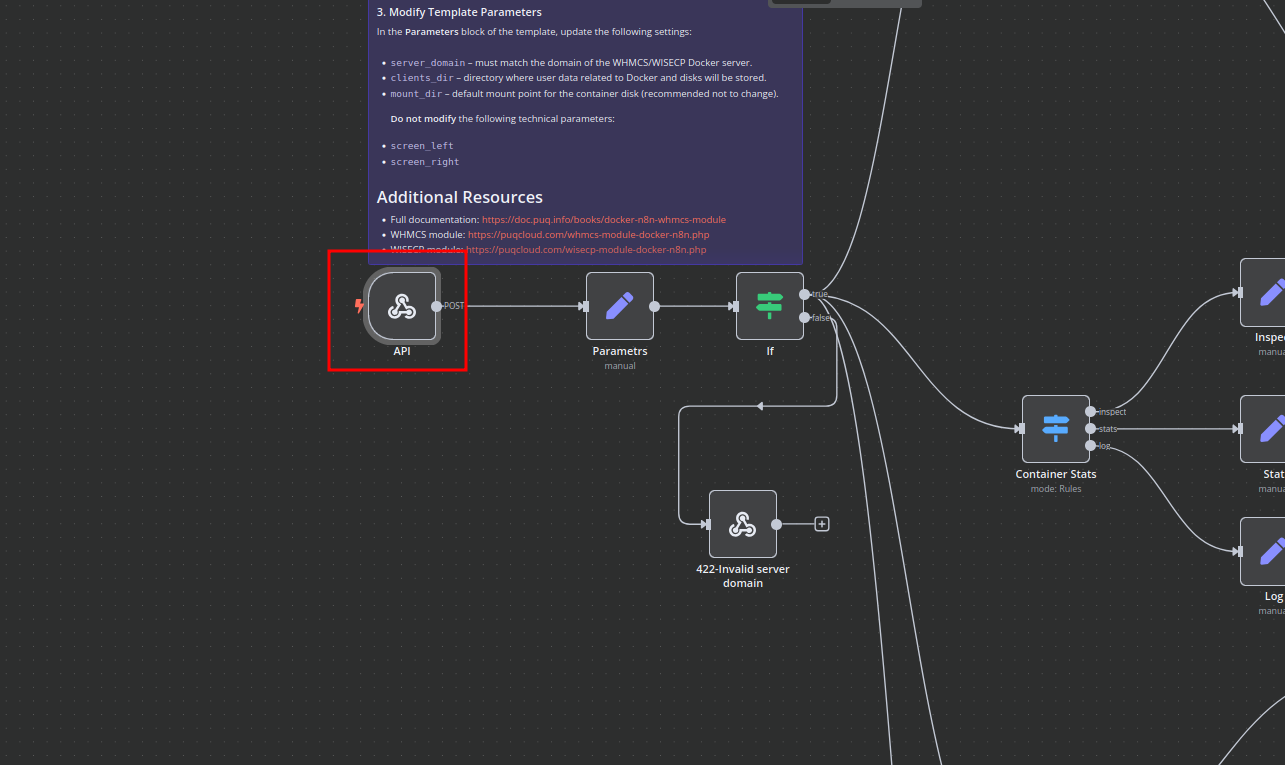
Modify Template Parameters
In the Parameters block of the template, update the following settings:
server_domain– Must match the domain of the WHMCS/WISECP Docker server.clients_dir– Directory where user data related to Docker and disks will be stored.mount_dir– Default mount point for the container disk (recommended not to change).
Do not modify the following technical parameters:
screen_leftscreen_right
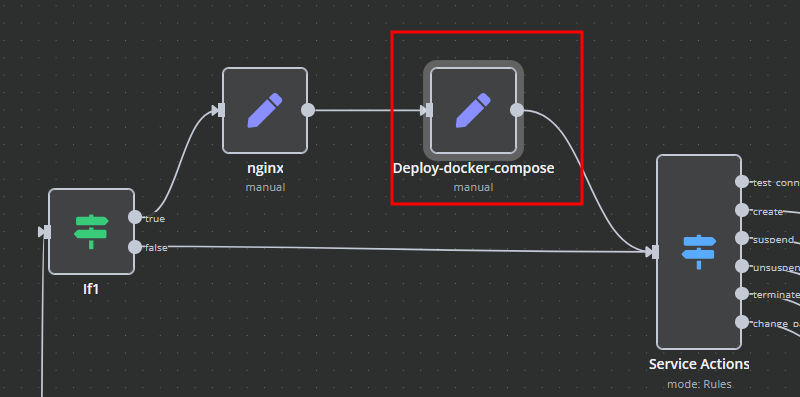
Deploy-docker-compose
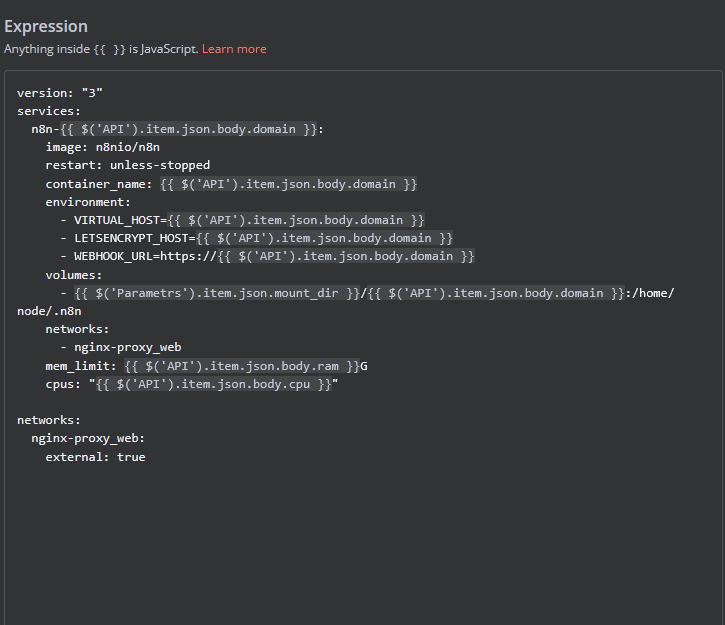
In the Deploy-docker-compose element, you have the ability to modify the Docker Compose configuration, which will be generated in the following scenarios:
- When the service is created
- When the service is unlocked
- When the service is updated
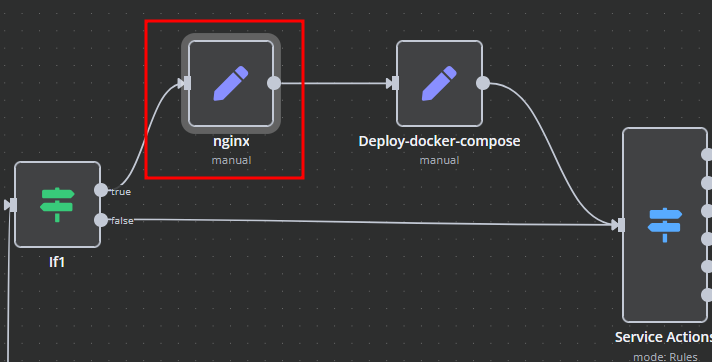
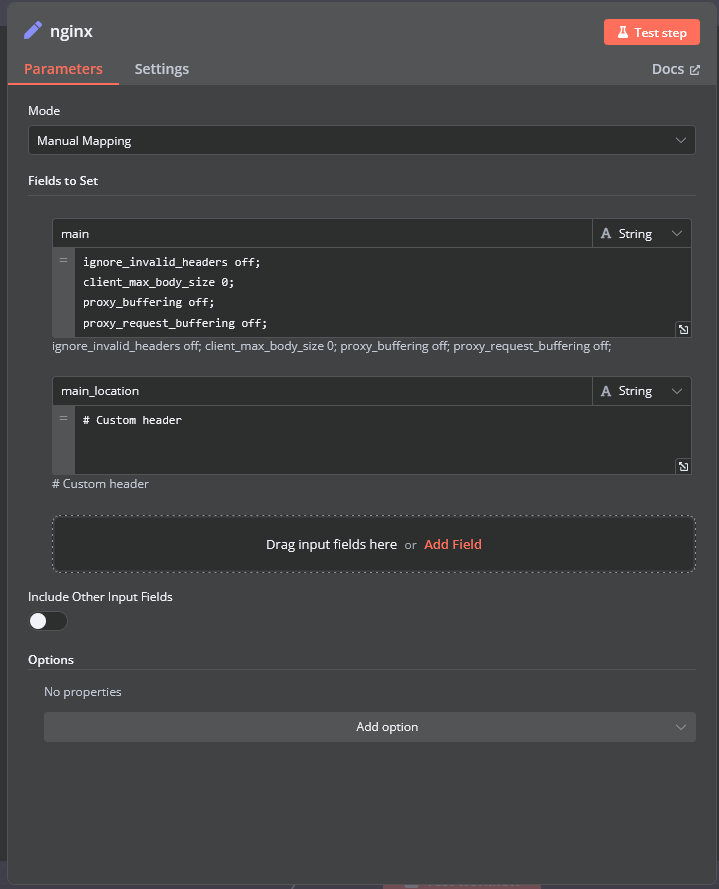
nginx
In the nginx element, you can modify the configuration parameters of the web interface proxy server.
- The main section allows you to add custom parameters to the server block in the proxy server configuration file.
- The main_location section contains settings that will be added to the location / block of the proxy server configuration. Here, you can define custom headers and other parameters specific to the root location.
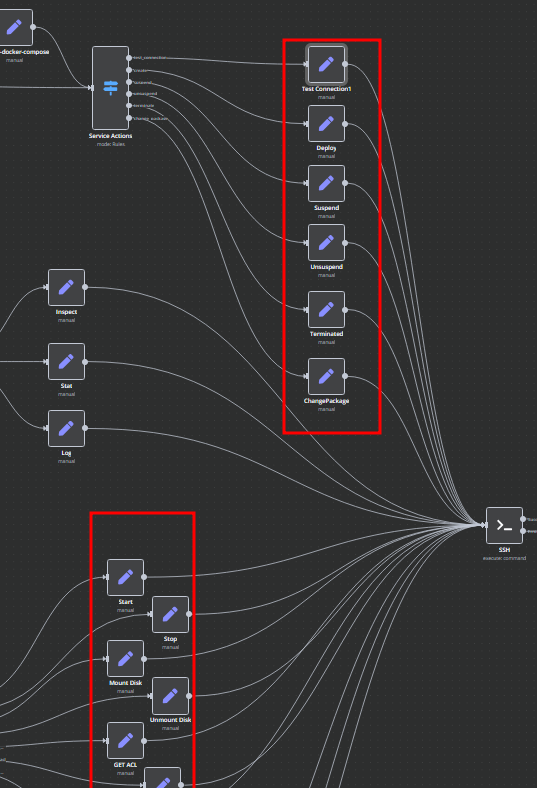
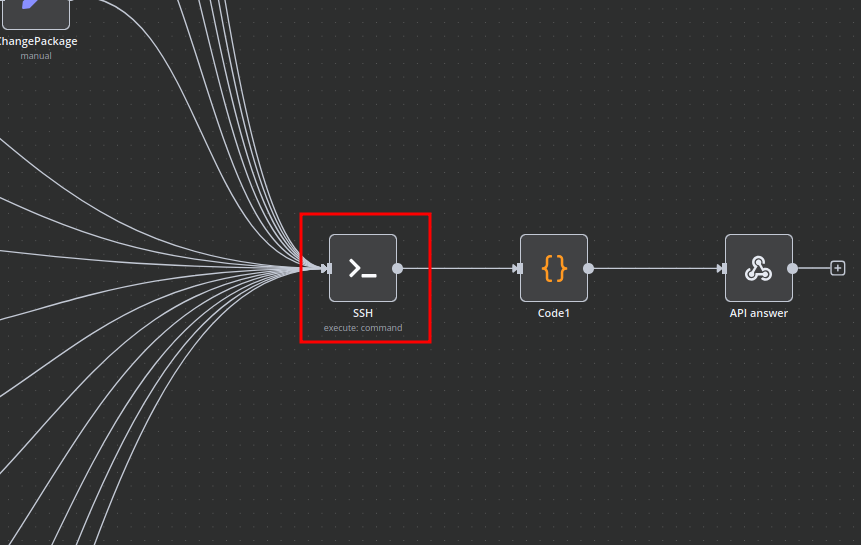
Bash Scripts
Management of Docker containers and all related procedures on the server is carried out by executing Bash scripts generated in n8n. These scripts return either a JSON response or a string.
- All scripts are located in elements directly connected to the SSH element.
- You have full control over any script and can modify or execute it as needed.
n8n Docker API Backend Deployment Workflow
This n8n workflow provides a robust and flexible solution for deploying and managing a Docker API backend. It acts as a central control point, allowing you to trigger deployments, execute commands, and receive structured responses, all through a simple webhook.
What it does
This workflow automates the following steps:
- Listens for a Webhook Trigger: The workflow starts by listening for incoming HTTP POST requests to a defined webhook URL. This acts as the entry point for triggering deployment actions.
- Conditional Routing (If): It then uses an "If" node to evaluate conditions based on the incoming webhook data. This allows for dynamic routing of the workflow based on specific criteria (e.g., different deployment environments, specific commands).
- Data Transformation (Edit Fields): An "Edit Fields (Set)" node is used to manipulate or prepare the data received from the webhook. This could involve extracting specific parameters, setting default values, or reformatting the payload for subsequent steps.
- Multi-path Conditional Logic (Switch): A "Switch" node provides more advanced conditional routing, enabling the workflow to execute different branches of logic based on various values within the processed data. This is useful for handling multiple distinct deployment scenarios or commands.
- Remote Command Execution (SSH): The "SSH" node is designed to connect to a remote server and execute commands. This is the core component for interacting with your Docker environment, allowing you to run
docker-compose up,docker pull, or any other necessary shell commands. - Custom Logic (Code): A "Code" node allows for the execution of custom JavaScript code. This provides extreme flexibility for complex data manipulation, custom validations, or generating dynamic commands before executing them via SSH.
- Responds to Webhook: Finally, the "Respond to Webhook" node sends a custom response back to the caller of the initial webhook, providing feedback on the execution status or results of the deployment.
- Informational Notes (Sticky Note): A "Sticky Note" is included for documentation within the workflow itself, likely containing important instructions or context for maintainers.
Prerequisites/Requirements
To use this workflow, you will need:
- n8n Instance: A running n8n instance to host this workflow.
- SSH Credentials: SSH credentials (private key or password) configured in n8n to connect to your Docker host server.
- Docker Host Server: A remote server with Docker and Docker Compose installed, accessible via SSH.
- Webhook Caller: An application or service capable of sending HTTP POST requests to the n8n webhook URL.
Setup/Usage
- Import the Workflow: Import the provided JSON into your n8n instance.
- Configure Webhook:
- Activate the "Webhook" trigger node.
- Copy the generated webhook URL. This is the endpoint you will send requests to.
- Configure SSH Credentials:
- Open the "SSH" node.
- Select or create new SSH credentials within n8n that can connect to your Docker host.
- Ensure the SSH user has the necessary permissions to execute Docker commands.
- Customize Logic:
- If Node: Adjust the conditions in the "If" node (node ID 20) to match your desired routing logic based on incoming webhook data.
- Edit Fields Node: Modify the "Edit Fields" node (node ID 38) to transform the incoming data as needed.
- Switch Node: Configure the "Switch" node (node ID 112) to handle different cases for your deployment scenarios.
- Code Node: Implement your custom JavaScript logic in the "Code" node (node ID 834) for advanced processing or command generation.
- SSH Node: Configure the commands to be executed on your Docker host within the "SSH" node (node ID 490). This is where you'll define your
docker-composecommands or other deployment scripts. - Respond to Webhook: Customize the response sent by the "Respond to Webhook" node (node ID 535) to provide meaningful feedback to the caller.
- Activate Workflow: Set the workflow to "Active" in n8n.
- Trigger Deployment: Send an HTTP POST request to the webhook URL with the appropriate payload to trigger your deployment logic.
Related Templates
Auto-create TikTok videos with VEED.io AI avatars, ElevenLabs & GPT-4
💥 Viral TikTok Video Machine: Auto-Create Videos with Your AI Avatar --- 🎯 Who is this for? This workflow is for content creators, marketers, and agencies who want to use Veed.io’s AI avatar technology to produce short, engaging TikTok videos automatically. It’s ideal for creators who want to appear on camera without recording themselves, and for teams managing multiple brands who need to generate videos at scale. --- ⚙️ What problem this workflow solves Manually creating videos for TikTok can take hours — finding trends, writing scripts, recording, and editing. By combining Veed.io, ElevenLabs, and GPT-4, this workflow transforms a simple Telegram input into a ready-to-post TikTok video featuring your AI avatar powered by Veed.io — speaking naturally with your cloned voice. --- 🚀 What this workflow does This automation links Veed.io’s video-generation API with multiple AI tools: Analyzes TikTok trends via Perplexity AI Writes a 10-second viral script using GPT-4 Generates your voiceover via ElevenLabs Uses Veed.io (Fabric 1.0 via FAL.ai) to animate your avatar and sync the lips to the voice Creates an engaging caption + hashtags for TikTok virality Publishes the video automatically via Blotato TikTok API Logs all results to Google Sheets for tracking --- 🧩 Setup Telegram Bot Create your bot via @BotFather Configure it as the trigger for sending your photo and theme Connect Veed.io Create an account on Veed.io Get your FAL.ai API key (Veed Fabric 1.0 model) Use HTTPS image/audio URLs compatible with Veed Fabric Other APIs Add Perplexity, ElevenLabs, and Blotato TikTok keys Connect your Google Sheet for logging results --- 🛠️ How to customize this workflow Change your Avatar: Upload a new image through Telegram, and Veed.io will generate a new talking version automatically. Modify the Script Style: Adjust the GPT prompt for tone (educational, funny, storytelling). Adjust Voice Tone: Tweak ElevenLabs stability and similarity settings. Expand Platforms: Add Instagram, YouTube Shorts, or X (Twitter) posting nodes. Track Performance: Customize your Google Sheet to measure your most successful Veed.io-based videos. --- 🧠 Expected Outcome In just a few seconds after sending your photo and theme, this workflow — powered by Veed.io — creates a fully automated TikTok video featuring your AI avatar with natural lip-sync and voice. The result is a continuous stream of viral short videos, made without cameras, editing, or effort. --- ✅ Import the JSON file in n8n, add your API keys (including Veed.io via FAL.ai), and start generating viral TikTok videos starring your AI avatar today! 🎥 Watch This Tutorial --- 📄 Documentation: Notion Guide Need help customizing? Contact me for consulting and support : Linkedin / Youtube
Tax deadline management & compliance alerts with GPT-4, Google Sheets & Slack
AI-Driven Tax Compliance & Deadline Management System Description Automate tax deadline monitoring with AI-powered insights. This workflow checks your tax calendar daily at 8 AM, uses GPT-4 to analyze upcoming deadlines across multiple jurisdictions, detects overdue and critical items, and sends intelligent alerts via email and Slack only when immediate action is required. Perfect for finance teams and accounting firms who need proactive compliance management without manual tracking. 🏛️🤖📊 Good to Know AI-Powered: GPT-4 provides risk assessment and strategic recommendations Multi-Jurisdiction: Handles Federal, State, and Local tax requirements automatically Smart Alerts: Only notifies executives when deadlines are overdue or critical (≤3 days) Priority Classification: Categorizes deadlines as Overdue, Critical, High, or Medium priority Dual Notifications: Critical alerts to leadership + daily summaries to team channel Complete Audit Trail: Logs all checks and deadlines to Google Sheets for compliance records How It Works Daily Trigger - Runs at 8:00 AM every morning Fetch Data - Pulls tax calendar and company configuration from Google Sheets Analyze Deadlines - Calculates days remaining, filters by jurisdiction/entity type, categorizes by priority AI Analysis - GPT-4 provides strategic insights and risk assessment on upcoming deadlines Smart Routing - Only sends alerts if overdue or critical deadlines exist Critical Alerts - HTML email to executives + Slack alert for urgent items Team Updates - Slack summary to finance channel with all upcoming deadlines Logging - Records compliance check results to Google Sheets for audit trail Requirements Google Sheets Structure Sheet 1: TaxCalendar DeadlineID | DeadlineName | DeadlineDate | Jurisdiction | Category | AssignedTo | IsActive FED-Q1 | Form 1120 Q1 | 2025-04-15 | Federal | Income | John Doe | TRUE Sheet 2: CompanyConfig (single row) Jurisdictions | EntityType | FiscalYearEnd Federal, California | Corporation | 12-31 Sheet 3: ComplianceLog (auto-populated) Date | AlertLevel | TotalUpcoming | CriticalCount | OverdueCount 2025-01-15 | HIGH | 12 | 3 | 1 Credentials Needed Google Sheets - Service Account OAuth2 OpenAI - API Key (GPT-4 access required) SMTP - Email account for sending alerts Slack - Bot Token with chat:write permission Setup Steps Import workflow JSON into n8n Add all 4 credentials Replace these placeholders: YOURTAXCALENDAR_ID - Tax calendar sheet ID YOURCONFIGID - Company config sheet ID YOURLOGID - Compliance log sheet ID C12345678 - Slack channel ID tax@company.com - Sender email cfo@company.com - Recipient email Share all sheets with Google service account email Invite Slack bot to channels Test workflow manually Activate the trigger Customizing This Workflow Change Alert Thresholds: Edit "Analyze Deadlines" node: Critical: Change <= 3 to <= 5 for 5-day warning High: Change <= 7 to <= 14 for 2-week notice Medium: Change <= 30 to <= 60 for 2-month lookout Adjust Schedule: Edit "Daily Tax Check" trigger: Change hour/minute for different run time Add multiple trigger times for tax season (8 AM, 2 PM, 6 PM) Add More Recipients: Edit "Send Email" node: To: cfo@company.com, director@company.com CC: accounting@company.com BCC: archive@company.com Customize Email Design: Edit "Format Email" node to change colors, add logo, or modify layout Add SMS Alerts: Insert Twilio node after "Is Critical" for emergency notifications Integrate Task Management: Add HTTP Request node to create tasks in Asana/Jira for critical deadlines Troubleshooting | Issue | Solution | |-------|----------| | No deadlines found | Check date format (YYYY-MM-DD) and IsActive = TRUE | | AI analysis failed | Verify OpenAI API key and account credits | | Email not sending | Test SMTP credentials and check if critical condition met | | Slack not posting | Invite bot to channel and verify channel ID format | | Permission denied | Share Google Sheets with service account email | 📞 Professional Services Need help with implementation or customization? Our team offers: 🎯 Custom workflow development 🏢 Enterprise deployment support 🎓 Team training sessions 🔧 Ongoing maintenance 📊 Custom reporting & dashboards 🔗 Additional API integrations Discover more workflows – Get in touch with us
Automate loan document analysis with Mistral OCR and GPT for underwriting decisions
LOB Underwriting with AI This template ingests borrower documents from OneDrive, extracts text with OCR, classifies each file (ID, paystub, bank statement, utilities, tax forms, etc.), aggregates everything per borrower, and asks an LLM to produce a clear underwriting summary and decision (plus next steps). Good to know AI and OCR usage consume credits (OpenAI + your OCR provider). Folder lookups by name can be ambiguous—use a fixed folderId in production. Scanned image quality drives OCR accuracy; bad scans yield weak text. This flow handles PII—mask sensitive data in logs and control access. Start small: batch size and pagination keep costs/memory sane. How it works Import & locate docs: Manual trigger kicks off a OneDrive folder search (e.g., “LOBs”) and lists files inside. Per-file loop: Download each file → run OCR → classify the document type using filename + extracted text. Aggregate: Combine per-file results into a borrower payload (make BorrowerName dynamic). LLM analysis: Feed the payload to an AI Agent (OpenAI model) to extract underwriting-relevant facts and produce a decision + next steps. Output: Return a human-readable summary (and optionally structured JSON for systems). How to use Start with the Manual Trigger to validate end-to-end on a tiny test folder. Once stable, swap in a Schedule/Cron or Webhook trigger. Review the generated underwriting summary; handle only flagged exceptions (unknown/unreadable docs, low confidence). Setup steps Connect accounts Add credentials for OneDrive, OCR, and OpenAI. Configure inputs In Search a folder, point to your borrower docs (prefer folderId; otherwise tighten the name query). In Get items in a folder, enable pagination if the folder is large. In Split in Batches, set a conservative batch size to control costs. Wire the file path Download a file must receive the current file’s id from the folder listing. Make sure the OCR node receives binary input (PDFs/images). Classification Update keyword rules to match your region/lenders/utilities/tax forms. Keep a fallback Unknown class and log it for review. Combine Replace the hard-coded BorrowerName with: a Set node field, a form input, or parsing from folder/file naming conventions. AI Agent Set your OpenAI model/credentials. Ask the model to output JSON first (structured fields) and Markdown second (readable summary). Keep temperature low for consistent, audit-friendly results. Optional outputs Persist JSON/Markdown to Notion/Docs/DB or write to storage. Customize if needed Doc types: add/remove categories and keywords without touching core logic. Error handling: add IF paths for empty folders, failed downloads, empty OCR, or Unknown class; retry transient API errors. Privacy: redact IDs/account numbers in logs; restrict execution visibility. Scale: add MIME/size filters, duplicate detection, and multi-borrower folder patterns (parent → subfolders).